Vitiligo

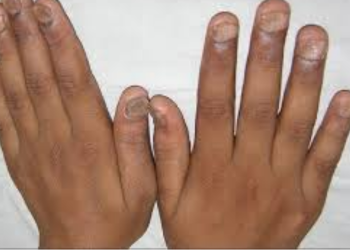
Vitiligo is a skin condition that causes your skin to lose its color or pigment. This causes your skin to appear
lighter than your natural skin tone or turn white. If you have vitiligo on a
part of your body that has hair, your hair may turn white or silver.
The condition occurs when your body’s immune system destroys
melanocytes.
Vitiligo usually starts with a few small white macules or patches that
may gradually spread over your body. Vitiligo typically begins on your hands,
forearms, feet and face, but can develop on any part of your body, including
your mucous membranes (the moist lining of your mouth, nose, genital and rectal
areas), your eyes and inner ears.
Sometimes, larger patches continue to widen and spread, but they usually
stay in the same place for years. The location of smaller macules shifts and
changes over time, as certain areas of skin lose and regain their pigment.
TYPES
- Generalized: This is the most common type of vitiligo that causes
macules to appear in various places on your body.
- Segmental: This type only affects one side of your body or one area,
such as your hands or face.
- Mucosal: Mucosal vitiligo affects mucous membranes of your mouth and/or
genitals.
- Focal: Focal vitiligo is a rare type where the macules develop in a
small area and don’t spread in a certain pattern within one to two years.
- Trichome: This type causes a bullseye with a white or colorless center,
then an area of lighter pigmentation, and an area of your natural skin tone.
- Universal: This rare type of vitiligo causes more than 80% of your skin
to not have pigment.
SYMPTOMS
- Patches of skin or mucous membranes that lose color. These can appear
white or lighter than your natural skin tone.
- Patches of hair on your body turn silver, grey or white.
Symptoms can be mild and only affect a small area of your body or severe
and affect a large area of your skin. Some people with vitiligo
experience itchy skin before
depigmentation starts.
CAUSES
- An autoimmune condition
- Genetic changes
- Stress
- Environmental triggers
PREVENTION
- Practicing safe sun exposure habits.
- Taking care of your skin by using a moisturizer daily.
- Avoiding stress or injury to your body.
- Managing any underlying autoimmune conditions.