Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic
disease, with inappropriately elevated blood glucose levels. About 537 million
adults across the world have diabetes. Too much glucose circulating in your
bloodstream causes diabetes, regardless of the type.
TYPES
- Type 2 diabetes: With this type, your body doesn’t make enough
insulin, and your body’s cells don’t respond normally to the insulin.
- Prediabetes: This type is the stage before Type 2 diabetes.
Your blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be
officially diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes.
- Type 1 diabetes: This type is an autoimmune disease in which your immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing
cells in your pancreas for unknown reasons.
- Gestational diabetes: This type develops in some people
during pregnancy.
SYMPTOMS
- Increased thirst and dry mouth.
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue.
- Blurred vision
- Unexplained weight loss
- Numbness or tingling in your hands or
feet.
- Slow-healing sores or cuts.
- Frequent skin infections.
CAUSES
Insulin resistance Several factors and cause
insulin resistance, including obesity, lack of physical activity, diet,
hormonal imbalances, genetics, and certain medications.
- Autoimmune disease
- Hormonal imbalances
- Pancreatic damage
- Genetic mutations
COMPLICATIONS
- Coronary artery disease
- Stroke
- Atherosclerosis
- Nerve damage, which can cause numbness,
tingling, and/or pain.
- Nephropathy
- Retinopathy, which can lead to blindness.
- Skin infections.
- Sexual dysfunction
- Hearing loss
- Oral health issues
DIAGNOSIS
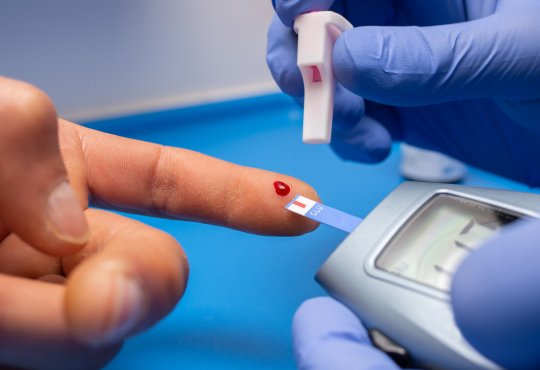
- Fasting blood glucose test For this test, you
don’t eat or drink anything except water for at least eight hours before the
test.
- Random blood glucose test
- HbA1C provides your average blood glucose level
over the past two to three months.
- Oral glucose tolerance test- for gestational
diabetes
MANAGEMENT
- Blood sugar monitoring
- Diet: Meal planning and choosing a healthy
diet
- Exercise
- maintain a healthy Weight
- Stress management
- Limit alcohol intake.
- Get adequate sleep
- Quit smoking
Welcome to u460539474_balsam Homeo, where we blend tradition with innovation to help you achieve optimal health. Our dedicated team of homeopathic doctors, rooted in the South Indian ethos, understands the challenges that come with managing Diabetes Mellitus. This lifestyle disease not only affects your physical health but can also impact your emotional well-being. We are here to provide effective solutions through homeopathic remedies for diabetes, empowering you to take control of your health journey.
Understanding Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes Mellitus is a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels due to the body's inability to produce enough insulin or utilize it effectively. There are various types of diabetes, including Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes, each requiring a unique approach to management. Symptoms may include excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. Left untreated, diabetes can lead to serious health complications, making early intervention crucial.
Our Homeopathic Approach
At u460539474_balsam Homeo, we take pride in our holistic approach to treating Diabetes Mellitus. Our homeopathic remedies for diabetes are formulated to not only address your blood sugar levels but also to promote overall well-being. We believe in treating the individual as a whole, considering your unique symptoms, lifestyle, and emotional health. By utilizing natural, safe remedies, we aim to restore balance and support your body’s innate healing processes.
Why Choose u460539474_balsam Homeo for Diabetes Management?
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Our expert homeopathic doctors in Sharjah take the time to understand your specific condition and develop a customized treatment plan that meets your needs.
- Natural and Effective Remedies: Our homeopathic treatments are made from natural ingredients, ensuring they are gentle and non-invasive while effectively managing your diabetes.
- Holistic Care: We focus on the interplay between physical health and emotional wellness, providing support that addresses all aspects of your life affected by diabetes.
Benefits of Homeopathic Remedies for Diabetes
- Support Blood Sugar Regulation: Homeopathic remedies can help stabilize blood sugar levels, reducing the need for conventional medications and their side effects.
- Promote Overall Wellness: Our treatments are designed to improve your overall health, enhancing your energy levels and vitality.
- Emotional Support: Living with diabetes can be challenging. We offer a supportive environment to help you navigate the emotional aspects of managing a chronic condition.
Empowering You to Manage Your Diabetes
In addition to our targeted homeopathic remedies for diabetes, we emphasize the importance of lifestyle modifications. Our doctors will guide you on nutrition, exercise, and stress management techniques that can enhance your overall treatment and support your health goals.
Start Your Journey to Better Health Today
If you’re looking for a compassionate and effective approach to managing Diabetes Mellitus, u460539474_balsam Homeo is here to support you. Our team of expert homeopathic doctors in Sharjah is committed to providing you with the tools and guidance you need to reclaim your health.
Schedule Your Consultation Now
Don’t let diabetes dictate your life. Visit our homeopathic clinic in Sharjah to explore the benefits of natural, individualized treatment options. Schedule a consultation with our expert homeopathic doctor today and take the first step towards a healthier, happier you.