Psoriasis
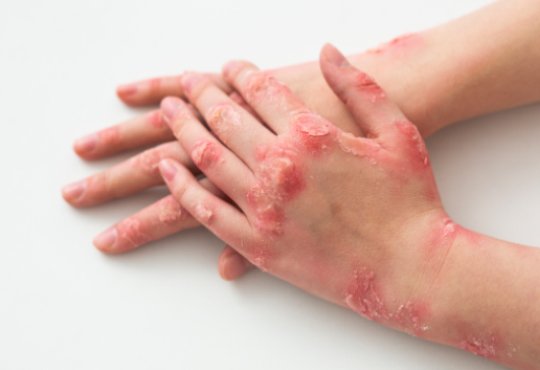
Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition that causes inflammation in your
skin. Symptoms of psoriasis include thick areas of discolored skin covered with
scales. These thick, scaly areas are called plaques.
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition,it can flare up unexpectedly
TYPES
- Plaque psoriasis:
Plaque psoriasis is very common it affects about 80% to 90% of people with
psoriasis have plaque psoriasis.
- Inverse psoriasis:
This type appears in your skin folds. It causes thin plaques without scales.
- Guttate psoriasis:
Guttate psoriasis may appear after a sore throat caused by a streptococcal infection.
It looks like small, red, drop-shaped scaly spots and often affects children
and young adults.
- Pustular psoriasis:
Pustular psoriasis has small, pus-filled bumps on top of plaques.
- Erythrodermic psoriasis:
This is a severe type of psoriasis that affects a large area of your skin. It
causes widespread skin discoloration and skin shedding.
- Sebopsoriasis: This type typically appears on your face and scalp as
bumps and plaques with a greasy, yellow scale. This is a cross between
psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis.
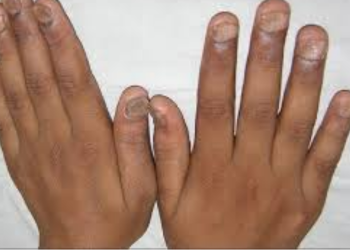
- Nail psoriasis: Nail
psoriasis causes skin discoloration, pitting and changes to your fingernails
and toenails.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Psoriasis and eczema are two
different skin conditions. Both conditions cause similar symptoms like
discolored skin, a rash, and itching. Psoriasis plaques cause areas of thick
skin covered in scales. Eczema causes a rash of dry and bumpy skin. Eczema also
typically causes more intense itching than psoriasis.
SYMPTOMS
- A rash or a raised
area of thick skin.
- The skin on the plaque is discolored.
- The plaque is scaly or flaky and sheds easily.
- Itchy skin.
- Cracked, dry skin.
- Skin pain.
- Nails that are pitted, cracked or crumbly.
- Joint pain.
CAUSES
An over-reactive immune system that
creates inflammation in your skin causes psoriasis. which you see on the surface
of your skin as skin plaques.The speed of new cells replacing old cells creates
scales and frequent skin shedding on top of skin plaques.
Psoriasis runs in families.
TRIGGERS
- Emotional stress.
- An infection (streptococcal infection).
- A skin injury like cuts, scrapes or surgery.
- Certain medications
- Changes in body temperature due to the weather.
MANAGEMENT
- Eating a well-balanced diet.
- Exercising regularly.
- Getting adequate sleep
- Not smoking.