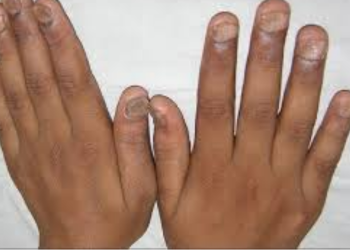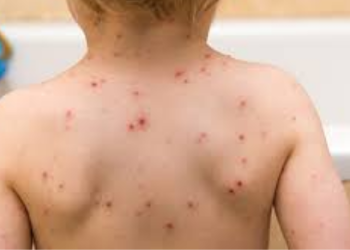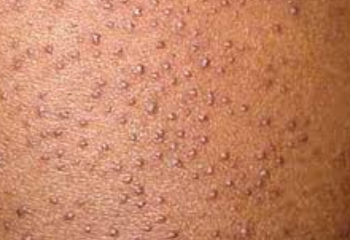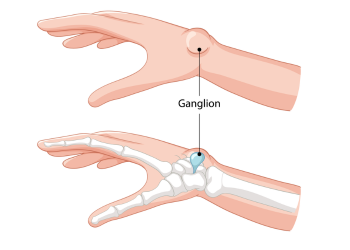
Ganglion cysts are lumps that most
often appear along the tendons or joints of the wrists or hands. They can occur
in the ankles and feet. Ganglion cysts are typically round or oval and are
filled with a jellylike fluid. They are not cancer.
Small ganglion
cysts can be pea-sized. They can change size. Ganglion cysts can be painful if
they press on a nearby nerve. Sometimes they affect joint movement.
For a ganglion cyst
that causes problems, homoeopathy is a safe option. It can be treated
non-surgically with homoeopathic medications. Often, the cysts grow and shrink
by themselves. Some go away on their own.
Symptom
Location. Ganglion
cysts most often develop along the tendons or joints of the wrists or hands.
The next most common locations are the ankles and feet.
Shape and size. Ganglion
cysts are round or oval. Some are too small to feel. The size of a cyst can
change, often getting larger over time with joint movement.
Pain. Ganglion
cysts are painless. But if a cyst presses on a nerve or other structures, it
can cause pain, tingling, numbness or muscle weakness.
Causes
No one knows what
causes a ganglion cyst. It grows out of a joint or the lining of a tendon and
looks like a tiny water balloon on a stalk. Inside the cyst is a thick fluid,
like the fluid found in joints or around tendons.
Risk factors
Sex and age. Ganglion
cysts can develop in anyone, but they most often occur in women between the
ages of 20 and 40.
Osteoarthritis. People who
have wear-and-tear arthritis in the finger joints closest to the fingernails
are at higher risk of developing ganglion cysts near those joints.
Joint or tendon injury. Joints or
tendons that have been injured are more likely to develop ganglion cysts
Diagnosis
During the physical
exam, press on the cyst to see if it hurts. Shining a light through the cyst
might show if it's solid or filled with fluid.
Imaging tests ,such
as an X-ray, ultrasound or MRI, can help confirm the diagnosis as well as rule
out other conditions, such as arthritis or a tumor.
Fluid drawn from
the cyst with a needle might confirm the diagnosis. Fluid from a ganglion cyst
is thick and clear.
Treatment
Ganglion cysts are
often painless and need no treatment.recommend watching the cyst for any
changes. If the cyst causes pain or gets in the way of joint movement, you may
need to:
Keep the joint from moving. Activity can
cause a ganglion cyst to grow. So wearing a brace or splint to keep the joint
still for a time might help. As the cyst shrinks, it may release the pressure
on nerves, relieving pain. But long-term use of a brace or splint can weaken nearby
muscles.
Drain the cyst. Draining the
fluid from the cyst with a needle might help. But the cyst can come back.
Surgery. This may be a
choice if other approaches don't work. Surgery involves removing the cyst and
the stalk that attaches it to the joint or tendon. Rarely, surgery can injure
the nearby nerves, blood vessels or tendons. And the cyst can come back, even after
surgery.
HOMEOPATHIC MEDICINE
Sulphur
Calcarea flouratum