Myelopathy is an injury to the
spinal cord caused by severe compression that may be a result of spinal
stenosis, disc degeneration, disc herniation, autoimmune disorders or other
trauma. When any part of the spinal cord is compressed, it causes nerve
dysfunction along the spinal cord causing pain, loss of balance and
coordination and numbness in the area around the compression point. Myelopathy
can occur in any area along the spinal cord. Types of myelopathy include:
Cervical myelopathy: Myelopathy that occurs in the
neck.
Thoracic myelopathy: Myelopathy that occurs in the
mid region of the spine.
Lumbar myelopathy: Not as common as cervical or
thoracic, lumbar myelopathy occurs in the lower region of the spine.
If left untreated, myelopathy can
lead to permanent spinal cord injury and nerve damage.
SYMPTOMS
When the spinal cord is
compressed or injured, it may cause a loss of sensation, loss of function, and
pain or discomfort in the area at or below the compression point. Symptoms of
myelopathy can vary based on where it occurs in the spine.
Myelopathy symptoms may
include:
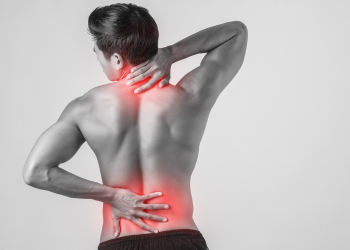
Pain in the lower back, neck, arm or leg
Tingling, numbness or weakness
Decreased fine motor skills, balance, and
coordination
Abnormal or increased reflexes in extremities
Difficulty walking
Loss of bowel or bladder function
CAUSES
Myelopathy is the result of
compression of the spinal cord and nerve roots caused by inflammation,
arthritis, bone spurs and spinal degeneration due to ageing. Myelopathy can
also take an acute form or result from a spine deformity at birth.
Common causes of myelopathy are:
Degenerative spinal conditions, such as spinal
stenosis
Central disc herniations
Autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis
Abnormalities, such as tumours, cysts, hernias, and
hematomas
Spinal injury or infection
Inflammatory disease
Radiation therapy
Neurological disorders
TREATMENT
Treatment for myelopathy depends
on the causes and other underlying conditions. Your treatment team will create
an individualized treatment plan to help relieve symptoms and slow down
progression.
Nonsurgical treatments may
include:
Physical therapy and exercise
Bracing
Taking medications
Interventional techniques such as nerve blocks
(spinal injections)
Epidural injections in the lumbar and cervical
spine
Activity modification
HOMEOPATHY MEDICINES
Homoeopathic medicines can manage
the symptoms of myelopathy effectively when used in the correct dosage
Theridion
Ruta
Kalium phosphoricum