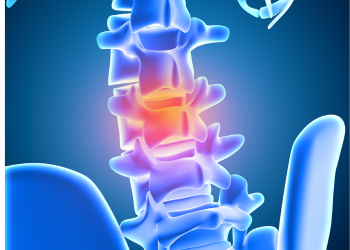
Radiculopathy is caused by
a pinched nerve in your spine. More specifically, it happens when one of your
nerve roots (where your nerves join your spinal column) is compressed or
irritated
Radiculopathy will cause
the area around the pinched nerve to feel painful, numb or tingly.
Depending on where along
your spine the pinched
nerve is,
Cervical
radiculopathy (neck).
Thoracic
radiculopathy (upper middle back).
Lumbar
radiculopathy (low back).
Radiculopathy vs. myelopathy
Both radiculopathy and
myelopathy are painful conditions involving your spine. Radiculopathy is a
temporary issue caused by a pinched nerve root near your spine. Myelopathy is the compression of your spinal cord caused by trauma, tumour,
degenerative disease or infection.
If it’s not treated,
myelopathy can worsen over time and cause permanent damage to your nerves.
Radiculopathy is a temporary issue that heals over time and often goes away
without treatment.
Radiculopathy
vs. spondylolysis
Spondylolysis is a weakness at the point where your vertebrae (the bones that
make up your spine) connect together. This can lead to small stress fractures that cause pain,usually in your lower back.
It usually affects teens going through growth spurts.
Radiculopathy can be
caused by bones in your spine moving out of place, but symptoms like pain are
caused when your nerve roots are compressed or irritated, and not by a broken
bone.
Radiculopathy vs. sciatica
Both radiculopathy and
sciatica are caused by pinched nerves.
The difference is which
nerves are pinched, causing the pain. Radiculopathy happens when a nerve along
your spine is irritated or compressed. Sciatica is the pain or discomfort you feel when your sciatic nerve gets
compressed or pinched.
Radiculopathy usually
hurts in the area of your back near the pinched nerve. Sciatica is a type of
radiculopathy that causes pain along your sciatic nerve in your lower back and
down your legs
Radiculopathy can affect
anyone, but it’s more common in people older than fifty
Radiculopathy is rare. At
the same time, neck pain and back pain, especially lower back
pain, are common problems.
The most obvious way
radiculopathy affects your body is the pain and other symptoms it causes around
your pinched nerve.
Depending on how severe
your symptoms are (and which type of radiculopathy you have) it might be hard
or uncomfortable to sit, stand or move. For example, if you have cervical
radiculopathy, it might be painful and difficult to move your neck.
Symptoms
Pain in the area around your affected
nerve.
Tingling.
Numbness.
Muscle
weakness.
Cervical radiculopathy: You might
have pain and other symptoms in and around your neck, but these symptoms can
radiate (spread out) to your arms and hands, too.
Thoracic radiculopathy: You’ll
likely have pain in and around your chest, including when you breathe in and
out.
Lumbar radiculopathy: The pain or numbness in
your lower back can spread to your legs.
Some radiculopathy
symptoms are similar to other, much more serious issues. Don’t ignore pain in
your chest, trouble breathing or numbness in your limbs.
CAUSES
Anything that compresses
or irritates the roots of your spinal nerves can cause radiculopathy,
including:
Traumas like
falls or car accidents.
Bone spurs are growing on one of your vertebrae.
A herniated
disc (also referred to as slipped, ruptured or
bulging discs
Getting older.
Diagnosis and Tests
Diagnose radiculopathy with a physical exam
and imaging tests. They’ll look at your back and spine, talk to you about your
symptoms and ask about the different sensations you’re feeling.
X-ray: An X-ray can show narrowing and changing alignment of your spinal
cord, as well as any spinal fractures.
Computed
tomography (CT) scan: A CT scan
shows 3D images and more detail of your spine than an X-ray can.
Magnetic
resonance imaging (MRI): An MRI can
show if damage to soft tissues is causing the nerve compression. It will also
show any damage to your spinal cord.
Electromyography
(EMG): An EMG measures electrical impulses in your
muscles. This can help determine if a nerve is working as it should. This helps
your healthcare provider know if your symptoms are caused by pressure on your
spinal nerve roots or if another condition (like diabetes) damaged your nerves.
Management and Treatment
Treatment depends on which
type of radiculopathy you have (where the pinched nerve is along your spine)
and how severe your symptoms are. Some people never need formal treatment if
their symptoms improve on their own in a few days or weeks.
Ice or heat: keep ice or apply heat to your back to reduce
swelling or relax tight muscles.
Adjusting your posture or physical therapy: Stretches and exercises that target the area around your spine can
help ease pressure on your nerves and relieve pain. Improving your overall
posture can help reduce stress on your spine and relieve your symptoms.
HOMEOPATHIC
MEDICINES
Rhus Toxicodendron
Arnica Montana
Hypericum
Self Care
Adjust your posture to make your daily routine
more comfortable. Stretches or exercises
to strengthen your core muscles, try to do them as often as recommended.
Don’t force yourself to do
anything that hurts while you’re recovering, though. It might make your
symptoms worse
Prognosis
You should expect to make
a full recovery from an episode of radiculopathy. It can be very painful and
inconvenient, but it’s usually a temporary condition.
It depends on what caused
your radiculopathy and which type you’re experiencing. In general, most people
feel better in a few weeks (or sooner). It might be longer if you have severe
symptoms or other conditions that affect your spine.
Prevention
Many of the causes of
radiculopathy can’t be prevented. Maintaining good spine health and posture can help prevent someof the degeneration that can lead to radiculopathy.
Homoeopathy is a system of
medicine where radiculopathy symptoms and pain intensity can be shortened it
also offers a mild and permanent cure for this condition